Two Type Scanning Technologies of Barcode Scanners
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form, which is extensively applied to transportation, logistics, retail, medical, administrative law enforcement, and many other industries. Barcodes can be divided into one-dimensional codes and two-dimensional codes. The information stored in 1D and 2D codes can be read by barcode scanners.

At present, the barcode scanning technology of the scanner device is mainly separated into two types: the laser method and the image method. The image method can be further divided into CCD (Charge Coupled Device) and CMOS.
Laser barcode scanner
Working principle
A laser diode emits a beam of light, irradiated on a rotating prism or a mirror that swings back and forth. The reflected light passes through the reading window and irradiates the surface of the barcode, returns to the reader after being reflected by the bar or blank, and is collected and focused by a mirror. Later, the light will be converted into an electrical signal by a photoelectric converter, and finally decoded by the scanner.

Pros
A laser barcode scanner has many advantages, such as low cost, stable technology, wide recognition, and simple data.
Cons
A laser barcode scanner cannot scan screens and QR codes.
Image barcode scanner
Working principle
CCD image barcode scanner uses one or more LEDs to emit light so that the light can cover the whole barcode. Then the image of the barcode is sampled by each individual photodiode and converted into an electrical signal that can be decoded, and the electrical signal compiles and decoded the sample.
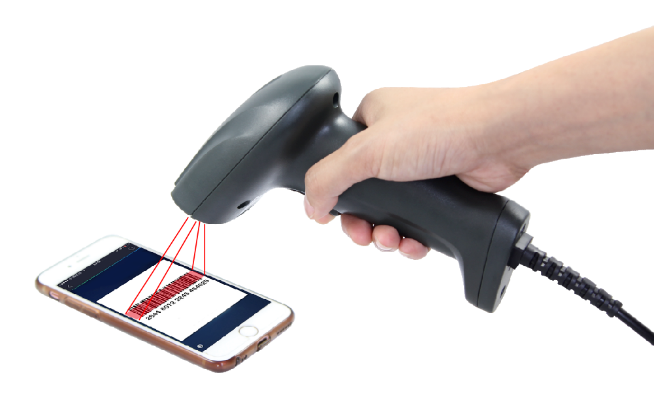

CMOS image barcode scanner uses photoelectric elements to convert the detected optical signal into an electrical signal, and then convert the electrical signal into a digital signal through an analog-to-digital converter and transmit it to the MCU of the scanner for decoding, and then transmit it to the computer to be deal with.

Pros
An image barcode scanner has better-corrupted barcode scanning, and it can read screens and 2D codes.
Taking advantage of CMOS scanning technology, HPRT develops handheld barcode scanners guns, fixed barcode scanners, and embedded barcode scanners. They are widely used in retail, logistic, healthcare, transportation, and other industries to scan and recognize 1D codes such as UPC, ENA, Code39, Code128, and 2D codes such as QR, DataMatrix, PDF-417, Aztec, and Max.