1D vs 2D Barcode Scanners: How to Choose?
From retail floors to expansive warehouses, barcode scanners are essential tools that drive efficiency and accuracy across various sectors. These scanned barcodes mainly fall into two categories: 1D and 2D. So, if you're considering opening a new store or purchasing scanning equipment for your warehouse, an important choice lies ahead: should you opt for a 1D or 2D barcode scanner? This article provides a detailed comparison between the two types of scanners, giving you the insights you need to choose the right one for your situation.

1D Barcode Scanners
1D barcodes, also known as linear barcodes, consist mainly of parallel lines of varying widths and gaps. These are the most widely used types of barcodes, such as UPC codes on consumer goods, ISBN codes on books, Code 128 on airline luggage tags, and Interleaved 2 of 5 codes in logistics and warehousing.
The main features of 1D barcodes are their simple structure and fast reading speed. However, they have limitations in data storage, typically holding up to 85 characters. There are mainly two types of 1D barcode scanners: laser scanners and CCD scanners.
● 1D Laser Scanners
These scanners use laser technology to read barcode information. The laser beam shines on the barcode, and the reflected light is captured and decoded. This method is fast and efficient but requires the barcode to be clear and undamaged. For worn or poorly printed barcodes, these scanners may not be as effective.
● 1D CCD Barcode Scanners
Also known as red light barcode scanners, these use CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) technology similar to digital cameras. They capture an image of the barcode for decoding, making them more suitable for reading damaged or poorly printed barcodes.
1D barcode scanners are widely used in retail, logistics, inventory management, healthcare, and libraries. For example, UPS extensively uses 1D barcode scanners for efficient package sorting and real-time tracking, handling millions of packages daily.
Overall, 1D barcode scanners are not only more cost-effective but also easier to operate. However, they are limited to reading 1D barcodes and can't decode the more information-rich 2D barcodes.
2D Barcode Scanners
Unlike 1D barcodes, 2D barcodes can store data both horizontally and vertically, offering significantly larger data storage. For example, a standard QR code can hold up to around 3,000 numerical characters or about 7,000 alphabetical characters. These 2D barcodes can store not only text and website URLs but even images. Common types of 2D barcodes include QR Code, PDF417, and DataMatrix.
With the rise of mobile payments, fixed barcode scanners and handheld 2D scanners are gaining popularity in retail supermarkets and dining establishments, primarily because they enable quick and secure transaction processing.

2D barcode scanners typically employ CMOS imaging technology. Unlike traditional laser scanning, CMOS technology captures a large amount of data in one go and processes it as an image, efficiently decoding the information. This technology excels at quickly and accurately parsing complex 2D barcodes while also easily handling various 1D barcodes.
2D barcode scanners boast excellent adaptability, accurately reading barcodes from a variety of surfaces and angles. They can scan barcodes and QR codes printed on paper, packaging films, and even capture QR codes displayed on digital screens.
Beyond retail, 2D barcode scanners are also widely used in healthcare for patient identification, in logistics for asset tracking, and in manufacturing for component verification. While 2D barcode scanners are generally more expensive, their comprehensive reading capabilities and efficiency make them the preferred choice across multiple industries.
1D vs 2D Barcode Scanners: A Comprehensive Comparison
1D and 2D barcode scanners each have their strengths, designed to meet different user needs. Below, we compare these two types of barcode scanners on several important dimensions to give you a more comprehensive understanding.
● Scanning Range
1D barcode scanners can read a variety of 1D barcodes, including UPC, EAN, Code 39, and Code 128. These scanners often employ laser technology and are particularly effective for reading paper-based barcodes. If your business mainly focuses on retail or warehouse management and deals primarily with 1D barcodes, a 1D scanner is a cost-effective choice.
2D barcode scanners, on the other hand, offer excellent backward compatibility. They can read both 1D and 2D barcodes and even recognize barcodes displayed on mobile and electronic screens. This makes them the go-to equipment for various sectors like mobile payments at counters, logistics supply chains, healthcare management, and retail management.
For instance, in hospitals, nurses use the HPRT N130 handheld 2D barcode scanner to scan patients' wristbands for identity verification before administering medication. This ensures that each patient receives the correct treatment plan. In blood test areas, staff use wireless scanners to read the 2D barcodes on blood transfusion tubes, effectively tracking the origin and destination of samples to prevent errors or mix-ups.
● Scanning Speed
1D Laser Scanners and 1D CCD Barcode Scanners usually require precise alignment with the barcode to effectively capture and decode information. This can be cumbersome in specific applications, especially when rapid scanning of multiple barcodes is needed. In contrast, 2D barcode scanners can scan from multiple angles, offering greater flexibility.
● Ease of Operation
When it comes to scanning distance, the capabilities of 1D and 2D barcode scanners can differ significantly based on brand and model. Generally speaking, 1D barcode scanners are confined to a shorter range, typically between 4 to 24 inches. In contrast, high-end 2D barcode scanners can perform accurate scans from much greater distances, providing added flexibility in environments that require multi-angle and distance scanning, such as large warehouses or hospitals.
As for error tolerance, 2D barcode scanners generally outperform their 1D counterparts. While 1D scanners may struggle with damaged or poor-quality barcodes, 2D scanners boast a higher error tolerance due to the additional data and redundancy information they contain. This makes them particularly useful in logistics centers where package barcodes might be compromised due to wear or stains.
HPRT N160BT: High-Performance 2D Barcode Scanner
The HPRT N160BT high-performance 2D handheld barcode scanner offers a reading accuracy of up to 3mil. It can swiftly and accurately read a variety of 1D and 2D barcodes, including those on paper, film packaging, and even electronic screens. Moreover, it supports a maximum scanning distance of 550mm.

Equipped with advanced auto-decoding technology and a million-pixel sensor, this wireless barcode scanner can accurately read even damaged or faded barcodes. This feature is especially beneficial in high-intensity, high-traffic environments like logistics centers or large retail stores.
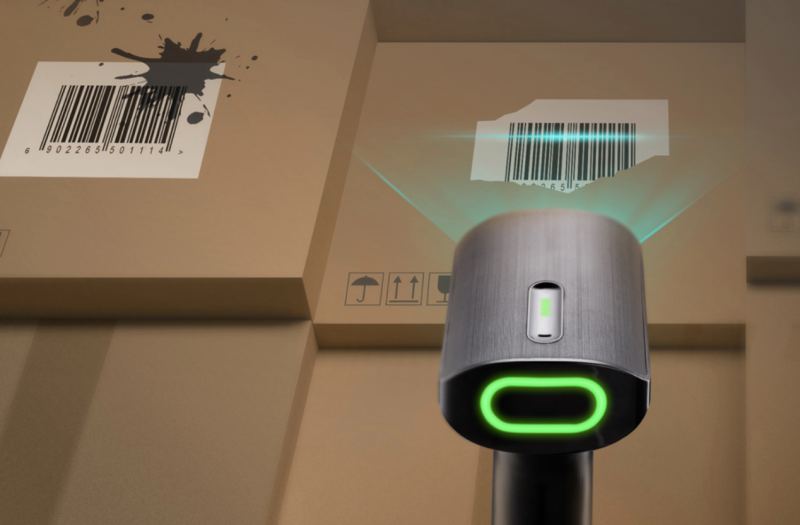

In terms of durability, this 2D barcode scanner also excels. Its 1.8-meter drop-resistant design ensures stability and longevity even under the most demanding conditions. A user-friendly LED light on the top intuitively indicates battery status, keeping you informed during use.
For connectivity, the barcode scanner supports Bluetooth connections with a transmission range of up to 100 meters and is compatible with multiple operating systems, offering plug-and-play convenience. Whether in a warehouse, supermarket, or hospital, the HPRT N160BT Bluetooth barcode scanner provides a stable and efficient scanning solution.
In summary, 1D barcode scanners are not only more cost-effective but also simpler to operate. However, they can only read 1D barcodes and are not suitable for 2D barcodes that contain more information. On the other hand, 2D barcode scanners excel in flexibility and error tolerance, making them particularly suitable for complex scenarios requiring efficient handling of a large amount of information.
Therefore, when you face the decision of choosing a barcode scanner, you should not only consider the price but also thoroughly evaluate your actual needs and application scenarios to make the most appropriate choice. As a reliable manufacturer of barcode scanners, we offer a diverse portfolio of high-quality products to fit every budget. Our expert team is always on standby to provide personalized consultations and tailor-made solutions for all your scanning needs.