Fixed Asset Tagging: Barcode Printer or RFID Printer?
The semi-annual or even quarterly fixed asset inventory often intimidates business managers, especially those managing larger scale enterprises with diverse assets and equipment in large quantities. As the scale of the enterprise expands and the number of personnel increases, the complexity of asset management continues to grow. How to quickly and accurately identify and track fixed assets has become an essential part of every business manager’s work.
Many companies opt to use label printersto print fixed asset tags for asset identification. Currently, there are two main identification methods on the market: using a barcode printer to generate fixed asset tags, or using an RFID label printerto print RFID tags for asset identification. So, how should we choose? This article explores these methods in detail, focusing on their respective advantages and offering guidance on their application.
Identifying Fixed Assets: Barcode Printer Vs. RFID Label Printer
A barcode printer is a device that can print barcode labels or QR code labels. Given that the service life of fixed assets generally exceeds 2 years, such fixed asset label printers typically use thermal transfer technology to print labels through ribbons. The printed labels can be preserved for a long time, are not easy to fade, and are wear-resistant.
Using a thermal transfer barcode printer, each fixed asset is equipped with a unique QR code, which serves as their "digital ID card". Just scan it with WeChat or other mobile application app, and you can immediately view the item’s number, name, specifications, brand, model, person in charge, and current status. During the fixed asset inventory, the information in the QR code is read by scanning devices such as mobile phones or scanners, thereby realizing the identification of the items.

An RFID label printer is a technology that uses radio frequency identification to track items. It consists of a chip and an antenna, which can be embedded or attached to items. RFID tags communicate with readers via radio waves, achieving the function of reading and writing data without contact.
After purchasing blank RFID tags, we need to use an RFID label printer to write label information. This process includes encoding and printing, encoding specific information into the RFID chip, and printing visible information on the label surface, such as text, barcodes, or QR codes. In this way, each RFID tag is given unique identity information, which can be used for tracking and managing various items.
RFID tags can store and transmit various types of data, such as product information, serial numbers, inventory status, etc. They can be widely used in logistics, supply chain management, inventory control, asset management, and identity recognition.
Choosing the Best Identification Method
The decision between these methods often hinges on a few factors: reading method, data type and capacity, and cost.
1. Reading method:
RFID tags can be read without direct line of sight and physical contact, and multiple tags can be read at high speed and long distance simultaneously. This has been fully applied in the borrowing and inventory of books in libraries. In contrast, QR codes need to be scanned by a camera, and only one QR code can be scanned at a time.
It is worth mentioning that RFID tags, used in conjunction with readers, can show significant advantages in tracking product status. For example, we can install readers at the entrances and exits of warehouses. When assets with RFID tags pass through, the reader can automatically read and record the information of the tags, thereby tracking and recording the movement path of the assets in real time.
2. Data type and capacity:
QR code labels usually contain information, URLs, text, contact information, and other types of data, with limited capacity, while RFID tags can store more types of information, including numbers, text, dates, times, etc. The capacity is also larger, and general RFID tags can store information from a few hundred bytes to a few thousand bytes.
By interacting with the backend database system in real time, it can also realize dynamic updating and reading of information. The information of QR code labels is usually static. Once generated and printed, its content cannot be directly changed.
3. Cost:
Compared with barcode printers and barcode labels, the cost of RFID label printers and RFID labels is relatively high. This is because RFID technology has more complex functions and higher technical requirements, and RFID tags themselves also need to integrate more advanced chips and antennas. Therefore, when choosing a label technology that suits your needs, you need to consider the match between cost, function, and demand.
In practice, for many small to medium-sized businesses, a practical and cost-effective solution to replace traditional handwritten fixed asset tags is to opt for a high-performance barcode printer, like the HPRT HT300. With system integration, businesses can achieve a one-item-one-code system for fixed assets. By scanning the printed QR code with mobile devices, they can interface with the system for smart inventory management.
The HPRT HT300 thermal transfer barcode printerhas a maximum printing speed of 127mm per second, supports various printing media, such as paper labels, PVC labels, and common fixed asset silver labels, etc.
Its maximum printing width is 108mm, and the length can reach 1200mm, meeting the printing needs of fixed asset labels of various sizes for enterprises. HT300 barcode label printer supports various types of barcode printing, including common Code 39, Code 93, Code 128, EAN13 barcodes, and QR Code, DataMatrix, and other QR codes.
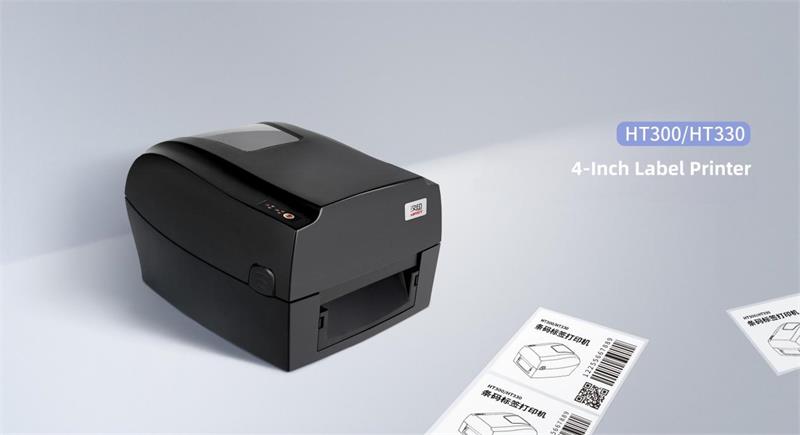

This QR code printer is equipped with multiple sensors, including gap detection and black mark detection, to ensure the accuracy of label paper feeding and printing. HT300 supports USB, serial port, Ethernet connection, and also provides a Bluetooth version, allowing you to print via mobile phones or tablets without a network connection.
In addition, HT300 is compatible with Windows, MacOS, Android, and iOS operating systems, allowing you to flexibly connect and use various devices.
Compared with RFID fixed asset marking technology, the method of printing QR codes with barcode printers is more suitable for scenarios with low requirements for reading speed and data capacity, such as small and medium-sized enterprises, schools, etc. And RFID label printers are more suitable for scenarios that require long-distance, high-speed, batch reading, and have higher requirements for data capacity, such as warehousing physics, manufacturing industry, medical industry, etc.
The HPRT iT4R is a typical UHF RFID printerused in the medical field. It supports various RFID label printing and encoding, suitable for EPC Class 1 Gen 2 (ISO18000-6C/6B) labels. iT4R has a high-precision label positioning system, which can accurately print and encode RFID labels, greatly improving the reading rate of labels.

In the medical industry, the HPRT iT4R 4-inch barcode RFID printer is widely used to print and encode RFID labels for medical devices and high-value consumables. Specifically, within an intelligent cabinet for medical consumables, the RFID labels produced by the iT4R assign each consumable a unique identification code, effectively implementing a one-item-one-code system. This approach is instrumental in facilitating the flow management of pharmaceutical consumables.
This unique identification system aids hospitals in achieving a comprehensive closed-loop management process, which spans from procurement to distribution, usage, and even return and loss tracking. By doing so, hospitals can accurately monitor the utilization of consumables, thereby mitigating wastage and loss.

Technological advancements have broadened the use of RFID technology across various sectors, demonstrating its robust capabilities. However, for certain scenarios, like in small to medium-sized businesses, a barcode printer for asset management might be more suitable. As technologies like the Internet of Things, big data, and AI continue to evolve, they enhance RFID’s potential for smarter, automated management. We eagerly anticipate the future innovations and breakthroughs RFID technology will bring.