Print Anti Counterfeit Labels with Barcode Printers
The global counterfeit goods issue is a significant concern, particularly in sectors such as luxury tobacco, cosmetics, and leather goods. These imitation products do not meet the standards of quality, safety, and effectiveness of their genuine counterparts, inflicting substantial harm to brand reputations. To combat this, security barcode labels, particularly security QR codes, have been introduced. These security labels assist consumers in effectively distinguishing counterfeit goods, thus reducing their distribution. Let’s explore the principles of QR code anti-counterfeiting and the process of using a barcode printer to generate security barcodes and print anti-counterfeit labels.

● Varieties of Security Barcode Labels
There’s a wide array of security barcode labels on the market, classified based on their material, manufacturing process, and functionality. These include holographic security labels, security watermark paper, Tamper-Evident Labels, and QR code labels, among others. QR code labels, due to their convenience, high level of security, and cost-effectiveness, find extensive use across various industries, including luxury tobacco, cosmetics, jewelry, and electronics.
● Understanding the Security QR Codes
The fundamental principle of QR code anti-counterfeiting is "one item, one code," implying that each product has a unique identification code. Once a product is labeled with a QR code, it becomes the exclusive "identity number" of that product. This number is traceable, and users can access comprehensive product information by scanning the code with their mobile phones. Naturally, counterfeit products cannot provide these details.

So, how can businesses mass-produce security QR codes?
1.Generate the QR code
Initially, you need to decide what information the QR code should encapsulate, such as product numbers, product descriptions, etc. You can also incorporate product highlights and marketing activities to promote the product and engage effectively with consumers.
Once the QR code content is finalized, use a QR code generator to transform this code into a QR code graphic. There are numerous online QR code generator tools to custom security labels.
To enable users to view the above content after scanning the QR code with their mobile phones, you also need to create a link or platform. During the QR code generation process, this link or platform address is embedded in the QR code. Once users scan this QR code, their mobile phones will automatically navigate to this link or platform, allowing them to view comprehensive product information. This way, users can not only swiftly obtain information but also have an intuitive experience.
2.Determine the label size and material
The size of the security label should be determined based on the size of the product itself or its packaging to avoid being excessively large or small, which may impact the aesthetics or usability of the product.
When selecting the material, carefully consider the product’s usage environment and whether it has wear-resistant, waterproof, and high-temperature resistant characteristics. Common materials for security QR code labels include paper, PET, PVC, synthetic paper, etc., each with its specific application scenarios and performance advantages and disadvantages.
For instance, when printing security QR codes for cosmetics, these products often face humid, greasy, or temperature-changing environments. Therefore, durable and waterproof materials, such as synthetic resin or high-quality thermal paper, are generally used to ensure the long-term clarity and stability of the QR code.
3.Print the QR code
When choosing a security label printer, consider purchasing a printer that can print high-definition QR codes and is easy to use and maintain, such as the HPRT HT300 4-inch barcode printer. It adopts an integrated movement design, stable, reliable, and low noise, ensuring your long-term printing. Moreover, its ribbon module design makes the ribbon installation operation simpler. Its large paper bin capacity, with a maximum paper roll outer diameter of up to 5 inches, avoids frequent paper loading interruptions during printing.
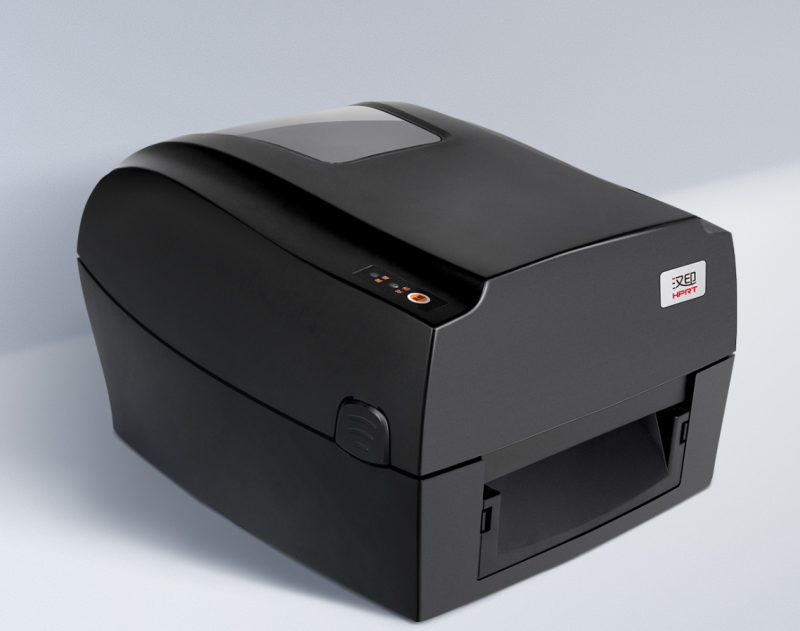

In barcode printing, it can print DataMatrix, QR Code, and all common one-dimensional codes such as Code128, EAN13, UPC-A, etc., providing clear and durable printing effects.
This desktop barcode printer has a rich detection function, such as seam mark detection, black mark detection, thermal head temperature detection, etc., to ensure neat and error-free printing. The HT300 thermal transfer barcode printer supports various printing media, including PET, PVC, synthetic paper, silver paper, etc., which are also commonly used materials for anti-counterfeit QR code printing. It’s a wise choice if your need to print security labels stickers.

If your printing demand is large, with a daily printing volume close to tens of thousands, such as electronic equipment, parts, and other product labels, then it is more suitable to choose an industrial-grade barcode printer. For instance, the HPRT Bingo industrial barcode printer is such a powerhouse of performance and efficiency, designed to cater to high-volume printing barcode security labels. It’s equipped with an advanced 32-bit processor chip that ensures smooth data processing, enabling it to handle complex tasks with ease.

One of the standout features of the HPRT Bingo is its impressive printing speed. It can reach up to 14 inches per second (ips) at a resolution of 203 dpi, making it one of the fastest in its class. For tasks that require higher resolution, the printer also offers options for 300 dpi and 600 dpi, ensuring that your labels are always sharp and clear.
The HPRT Bingo also prides itself on its substantial ribbon capacity, which can house a ribbon up to 450 meters in length. Additionally, it can accommodate a printing medium with a maximum outer diameter of 10 inches. These features significantly reduce the necessity for regular ribbon and printing medium replacements, thereby enhancing productivity and minimizing downtime.
To further enhance anti-counterfeiting efforts, some merchants also use QR codes in conjunction with scan counters. Whenever a user scans this QR code, the system records it. When consumers scan the QR code to verify the authenticity of the product, the scanning counter can record the number of scans in real-time. If it shows that this is not the first scan, then consumers can judge the product as a counterfeit, indicating that someone has cloned the genuine product’s QR code for counterfeiting.
Amidst the swift advancements in anti-counterfeiting label technology, the use of barcode printers to generate QR codes has emerged as a crucial instrument. However, this is just part of the digital anti-counterfeiting journey we are experiencing. Future anti-counterfeiting may combine more advanced technologies, such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, blockchain, etc., to achieve higher levels of anti-counterfeiting and traceability functions.
For example, using blockchain technology to ensure the immutability of information and improve the accuracy of anti-counterfeiting. As we face more complex counterfeit and inferior problems, we need smarter and more comprehensive anti-counterfeiting solutions, which will be the direction of our future efforts.