RFID Technology in Action: Uplifting User Experiences and Streamlining Management in Libraries
Mysterious and often seen as complex and high-tech, the term ’RFID’ is synonymous with concepts like the Internet of Things (IoT) and industrial printers. Yet, its influence seamlessly permeates our daily lives. For instance, the quick book identification process at your local library during a weekend visit relies on RFID technology. But what precisely is an RFID label, and how do libraries create and utilize these labels? Let’s explore these questions together.

● Understanding RFID Labels
RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is an advanced identification technology that enables touch-free reading without requiring direct sightlines.
An RFID label, a small electronic device affixed to objects, contains at least one radio frequency chip and an antenna. This combination allows communication via radio waves with a reading device, thereby enabling object tracking and management.
Think of an RFID label as an "electronic tag", much like the ones you find on clothing when shopping. These tags, typically detailing price, size, and material, could be replaced with RFID labels that act as miniature electronic notebooks storing more comprehensive information such as production date, supply chain data, and even your clothing preferences.
In comparison to traditional one-dimensional barcodes, RFID labels boast several benefits. They can be recognized without the need for precise alignment by a scanning device, as their radio wave communication means they can be read easily, even in environments with obstacles. What’s more, multiple labels can be read simultaneously.
Moreover, RFID labels can hold an extensive amount of data, ranging from hundreds to thousands of bytes. Additionally, the information on RFID labels can be updated at any time, offering superior flexibility.
● RFID Labels: The Library Application
1. Borrowing Books
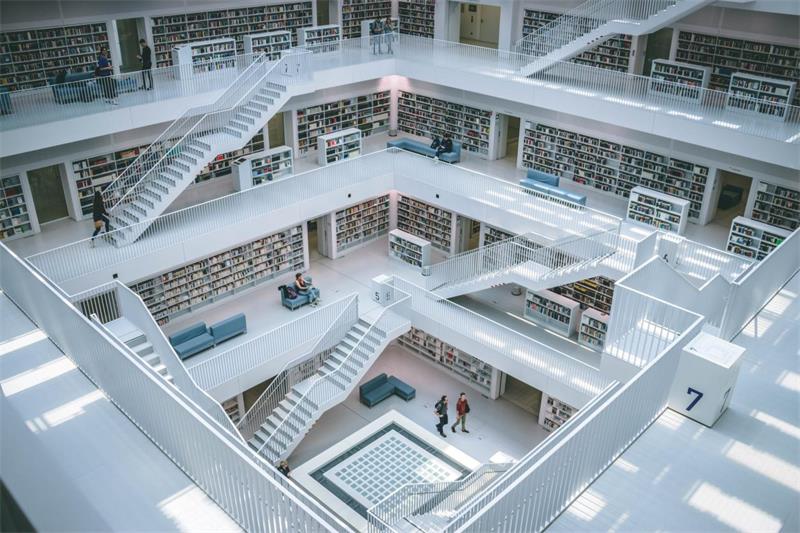
Modern-day municipal and university libraries extensively use RFID tags for book management. Libraries are fitted with self-service book borrowing and returning Kiosks. Users simply insert their library card, place the books they wish to borrow in the book-sensing area, and the machine promptly displays the information of the borrowed books.

The efficiency comes into play as the machine recognizes a stack of books without scanning them individually. Before RFID labels, libraries utilized barcodes for book borrowing, requiring patrons to scan each book separately—an inefficient and time-consuming process. If barcodes were damaged or unclear, patrons had to seek staff assistance, further slowing the process.
Thanks to RFID library labels, self-service checkouts with RFID readers can now read multiple labels simultaneously, greatly improving efficiency. Plus, RFID labels are robust and durable, as their chips and antennas are typically embedded within plastic or paper labels, shielding them from external elements.
When a book is borrowed, the library’s RFID system alters the book’s status to ’borrowed’—a process often referred to as "demagnetization". The status reverts when the book is returned. If a book is attempted to be taken out of the library without demagnetization, an alarm will sound at the exit, providing an effective deterrent against theft.
2. Inventory and Organization of Books
RFID labels can be recognized without contact, even through obstacles like non-metallic and non-liquid materials, enabling long-distance identification. For large libraries, using RFID scanning for inventory greatly lightens the workload for librarians and speeds up the process.
The introduction of smart shelves, equipped with RFID reader antennas that can track books labeled with RFID tags, has further optimized library management. By integrating these shelves with library management software systems, the data from the book tags can be transferred to the management system, helping staff quickly locate misplaced books.
● Printing RFID Labels
Libraries often use specialized RFID printers, typically divided into industrial and desktop categories.
Industrial RFID printers are suitable for high-volume and intensive printing environments like factories and warehouses. They offer high-speed printing and durability. For instance, the HPRT Bingo, a high-performance industrial RFID printer, is ideal for complex industrial environments such as manufacturing, logistics, and warehouse management. It’s used to print labels for goods, packing, logistics tracking, warehouse management, production lines, and more.
Desktop RFID printers, on the other hand, are suitable for environments with lower printing volume and durability requirements, like retail, healthcare, and offices. They can print labels for asset tracking, identity verification, medical wristbands, book RFID tracking, etc.
Most libraries, given their printing volumes, opt for desktop printers. The IDPRT iT4R, a professional UHF RFID barcode printer, is a prime example. It can print and encode ultra-high-frequency (UHF) book RFID electronic labels.
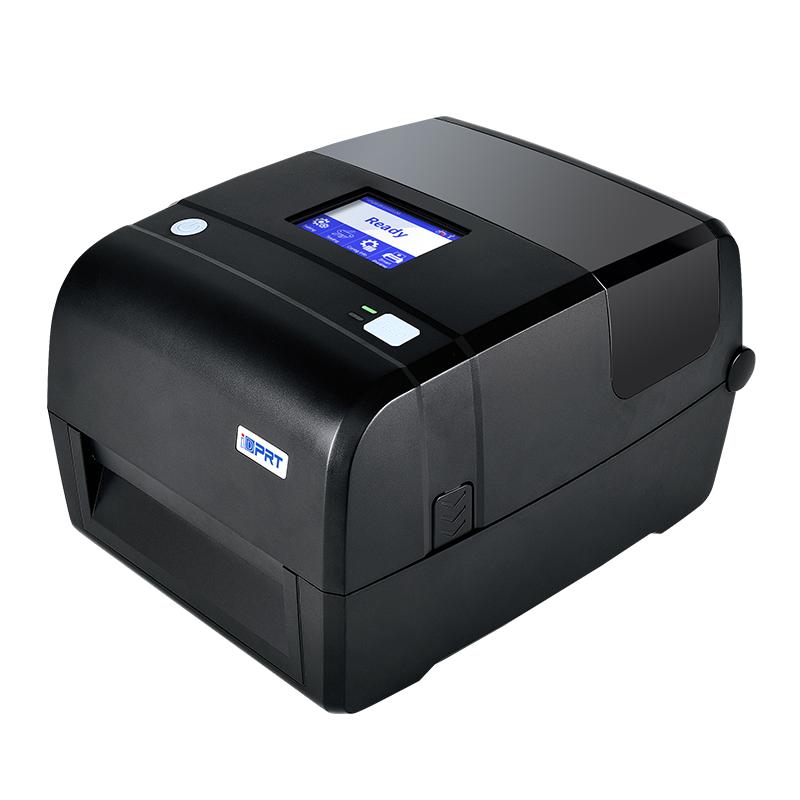

With an advanced chip and substantial storage space - 128MB RAM and 256MB Flash - this RFID printer boasts faster processing speed and higher computing power, easily encoding a multitude of different RFID labels.

It offers 203dpi and 300dpi printing precision, an easy-to-replace print head, and supports a maximum printing width of 104mm, fulfilling the requirements for printing book RFID labels.
The IDPRT iT4R RFID label printer features a 3.5-inch TFT LCD, touch screen design, and intuitive button operation, facilitating more convenient and quicker printing.

Connection options include the conventional USB and Ethernet, but its unique USB HOST option enables offline operation. For users with mobile printing needs, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi interfaces can also be optionally equipped.
RFID technology has already made a substantial impact on library efficiency, enhancing book lending, management, and maintenance processes. Yet, this is merely the tip of the iceberg. With ongoing technological advancements, RFID is poised to unleash immense potential in areas like the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence, paving the way for more sophisticated application systems. We eagerly anticipate the future developments of RFID technology and look forward to exploring them together!