The Power of Integration: Thermal Transfer Label Printers and IoT
The rapid changes in today’s business environment have driven companies to continuously seek innovative ways to improve their supply chain management. One important innovation is the integration of thermal transfer label printers and Internet of Things (IoT) technology. This powerful combination enables real-time tracking of products, assets, and equipment, bringing many benefits. Let’s explore together how thermal transfer label printers are cleverly integrated into the world of IoT.
Understanding Thermal Transfer Label Printers
At its core, a thermal transfer label printer employs heat to transfer ink from a ribbon onto a label. This process yields high-quality, durable labels that can withstand fading, smudging, and other types of damage. Although thermal transfer printers can be more expensive than direct thermal alternatives, they offer numerous benefits, such as the production of long-lasting, high-quality labels that remain resilient under various environmental conditions.
Integrating IoT Devices with Thermal Transfer Label Printers
Integration of thermal transfer label printers with IoT devices such as RFID readers, tags, barcode scanners, and sensors unlocks a wealth of possibilities. RFID tags embedded in labels facilitate real-time tracking, while barcode scanners contribute to improved inventory management and error reduction.
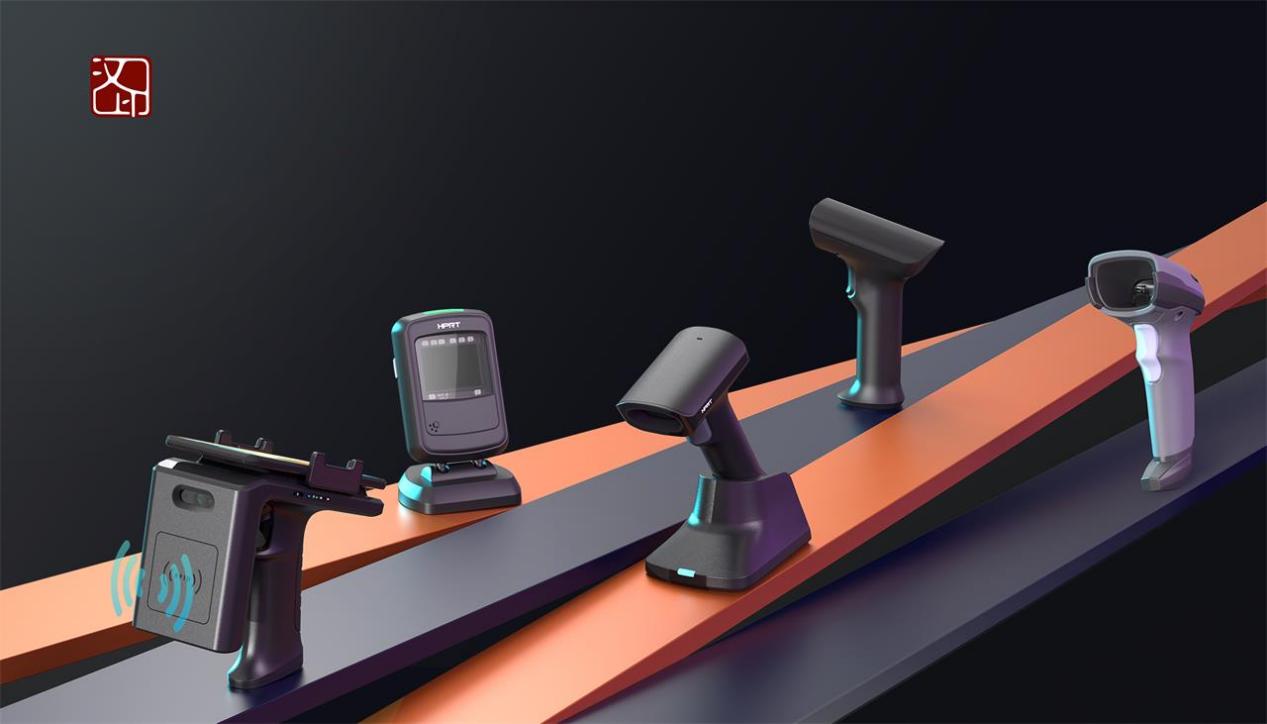

HPRT Glory, 4-inch industrial barcode printer series, can easily accomplish batch printing of RFID tags. This printer uses advanced chips delivering strong storage performance, and is equipped with a 3.5-inch color display and universal interfaces, making it convenient for users to operate.

IoT Applications: Thermal Transfer Label Printers in Action
Many applications in the Internet of Things utilize thermal transfer label printers to mark and track products, assets, and equipment. These applications can be grouped into four main categories:
a. Product labeling and tracking
Thermal transfer label printers are capable of accurately labeling and tracking products throughout their production and delivery process. For example, pharmaceutical manufacturers in the medical industry utilize thermal transfer label printers to mark and print information such as serial numbers, expiration dates, ingredients, barcodes, and usage instructions on drug bottles, boxes, and packaging. This helps to effectively track the production, transportation, and sale of drugs, preventing counterfeiting and loss.
b. Asset management
Businesses can utilize thermal transfer label printers to mark and track their assets, allowing for better management and protection in the Internet of Things. For instance, some domestic manufacturers use this technology to print labels for equipment and tools, marking their location, usage records, and maintenance requirements. This helps businesses understand the status and location of their assets, improving production efficiency and asset utilization.
c. Equipment tracking and maintenance
Thermal transfer label printers can also be used for equipment tracking and maintenance, ensuring high-performance and adherence to maintenance schedules. Some airlines utilize thermal transfer label printers to print labels for their aircraft and equipment, marking their components and maintenance history, ensuring equipment safety and efficient operation.
d. Inventory management
Many businesses use thermal transfer label printers to label and track their inventory in the Internet of Things, allowing for better management and control of their stock levels and locations. For example, Walmart uses these labels to monitor their inventory levels and location in real-time, ensuring optimal inventory management and reducing backlog or out-of-stock situations.
Advantages of Thermal Transfer Label Printers in IoT
By integrating thermal transfer label printers into the Internet of Things, companies can enjoy numerous benefits. Firstly, this combination enables quick, efficient, and accurate marking and tracking, leading to enhanced overall performance and work efficiency.
One of the world’s largest container shipping company, Maersk has adopted thermal transfer labels on shipping containers and pallets, greatly improving the tracking efficiency of the logistics department.
Secondly, thermal transfer label printers can boost inventory management efficiency by automatically marking and tracking inventory, reducing losses and waste, while also improving inventory turnover rates.
In addition, these label printers can enhance companies’ compliance with regulations. In the food industry, for example, companies can utilize thermal transfer label printers to print food labels that comply with regulatory requirements and update and monitor them in real-time using IoT technology to ensure compliance with hygiene standards and quality requirements.
Challenges and Solutions in IoT Thermal Transfer Label Printers
Despite the advantages, thermal transfer label printers for IoT applications may present challenges such as legacy system integration, data security, privacy concerns, and issues of cost and scalability. However, innovative solutions like cloud-based labeling systems, data security protocols, and partnerships with reputable label printer vendors can help businesses overcome these obstacles.
The Future of Thermal Transfer Label Printers and IoT
Technological advancements and material innovations are poised to drive growth and progress in the thermal transfer label printer industry. RFID technology, QR codes, and eco-friendly label materials will contribute to improved tracking and traceability while addressing environmental concerns. Automation and digitalization will also play a pivotal role in streamlining labeling processes and enhancing efficiency. As a result, the global thermal transfer label printer market is expected to expand, fueled by increasing demand for safe and efficient labeling in IoT applications.
The integration of thermal transfer label printers and IoT technology has changed the game rules for supply chain management. Companies need to have a deep understanding of the basic principles of thermal transfer label printers and their applications in IoT, as well as mastering the methods of integrating them with IoT devices, in order to optimize supply chain management and achieve more efficient and reliable supply chain management.