Complete Guide to Direct Part Marking (DPM), DPM Codes and Scanners
Barcode labels are a standard method for tracking and tracing products within the manufacturing industry. However, for certain components and parts, manufacturers and factories opt for Direct Part Marking (DPM) codes, which are directly marked on the surfaces bypassing the use of adhesive labels.
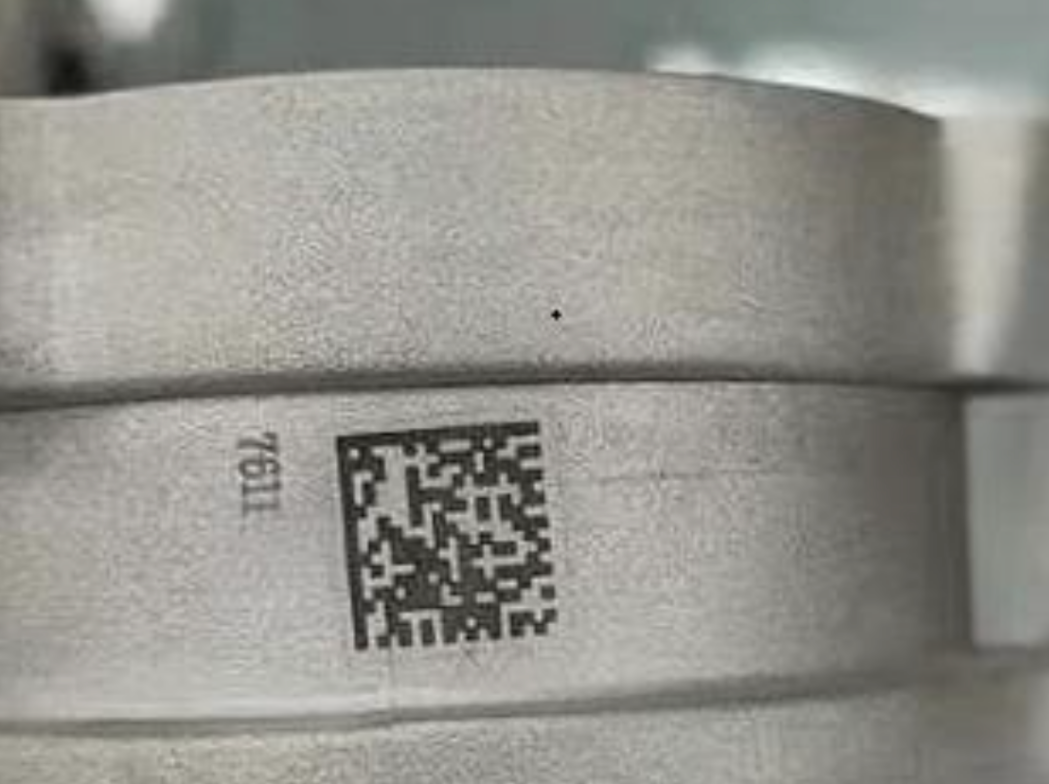

This method prompts several important questions: What exactly are DPM and DPM codes? What are their defining characteristics? And how can these codes be scanned effectively? Let's explore these questions in detail.
What is Direct Part Marking (DPM)?
Direct Part Marking (DPM) is a method used to permanently mark parts and components with identification codes onto part surfaces, typically 2D codes, for tracking and traceability.
It solves issues related to the durability of traditional barcode labels, such as wear and tear, detachment, and poor resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosive environments.
The marked 2D barcodes often store critical data like production dates, batch numbers, and serial numbers, allowing for the permanent tracking and tracing of components.
Common Applications of Direct Part Marking
● Automotive industry: Identification of automotive parts such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, crankshafts, and connecting rods.
● Aerospace industry: Marking of components like fuselages, wings, and engines.
● Electronics industry: Identifying electronic components such as chips, capacitors, and resistors.
● Mechanical industry: Marking of parts like bearings, gears, and machine tools.
Types of Direct Part Marking Techniques
● Laser Etching: Uses lasers to heat, melt, or vaporize material, creating a high-precision, durable mark on metals, plastics, and ceramics. Although highly effective, this method can be cost-prohibitive due to expensive equipment.
● Dot Peen Marking: Involves high-speed electromagnetic pins that strike the material surface to form indented or protruding dot patterns. This method is durable and simple to operate but can damage the surface of delicate parts.
● Chemical Etching: Utilizes chemical agents to corrode the material surface, creating a clear and high-contrast mark. While the marking clarity is high, the process is slower and poses safety risks due to the chemicals involved.
● Inkjet Marking: Directly prints codes on component surfaces with ink. Inkjet coding excels in speed and versatility across diverse materials but offers less durability compared to other marking techniques.
What is a DPM Code?
A DPM code is a unique identifier or barcode applied directly to a product's surface through direct part marking, commonly on materials such as metal or ceramics.
These barcodes are generally compact, for instance, those created using laser printing typically range in size from 0.5mm to 10mm.
Among the various 2D barcode options for Direct Part Marking (DPM), DataMatrix codes shine brightest due to their exceptional features:
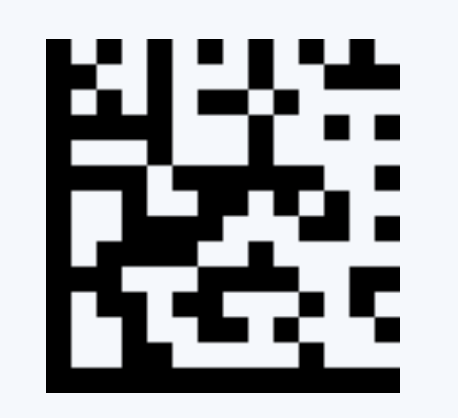

1. High Data Capacity
These codes efficiently store vast amounts of information in a compact area, including details such as part numbers, batch numbers, product parameters, technical specifications, and manufacturer data.
This feature is particularly valuable for electronic components and precision instruments, where barcode sizes may need to be less than 2mm.
2. Robust Error Correction and Durability
DataMatrix codes can remain readable even if they are partially damaged. This resilience is vital in the manufacturing industry, where DPM codes are often subjected to extreme conditions such as high temperatures, pressures, corrosion, and abrasion.
In essence, DPM codes ensure a permanent and durable mark on component surfaces. They offer excellent resistance to wear and detachment, effectively prevent counterfeiting and tampering, and support the traceability of various components across the manufacturing sector.
How to Scan a DPM Code?
Scanning a DPM code requires a specialized DPM scanner. Unlike traditional barcode scanners, DPM scanners employ advanced imaging technology to overcome the reflective glare of metal components and effectively read 2D barcodes like DM codes, even on curved or irregular surfaces.

We highly recommend the HPRT N180 handheld DPM barcode scanner. This industrial handheld scanner can decipher laser-etched, dot peened, and inkjet-printed DPM codes. The HPRT N180 DM scanner offers:
● Advanced DPM Barcode Decoding Algorithm: Equipped with a million-pixel resolution, this scanner delivers 3mil precision for rapid and precise detection of various barcode types. It effectively reads smudged, highly reflective DPM codes, high-density, and low-contrast 2D barcodes, even on the curved surfaces of metal and ceramic materials.
● Tri-Color Illumination and Laser Crosshair Focusing: These features enhance barcode contrast, significantly improving scan speed.
● Vibration Alert: Ideal for noisy environments or settings where silence is required.
● Robust Integrated Design: With a drop resistance of 2.4 meters and an IP65 protection rating, the scanner is built to withstand tough conditions.
The HPRT N180 Direct Part Marking (DPM) barcode scanner supports various modes such as sensor-based and continuous reading, making operations more convenient. This DPM scanner also features multiple connectivity options, including RS-232, USB keyboard, and USB virtual COM port.
As a reliable part marking technology, DPM codes are a crucial tool for product traceability and anti-counterfeiting in the manufacturing industry. The HPRT N180 direct part marking scanner, with its exceptional scanning capabilities, further elevates the effectiveness of DPM codes, guaranteeing seamless data capture and enhanced product integrity.
Experience the precision and efficiency of our DPM scanner products. Contact us today for a personalized consultation.